India's Power Sector Analysis: Organizing Bodies & Key Players
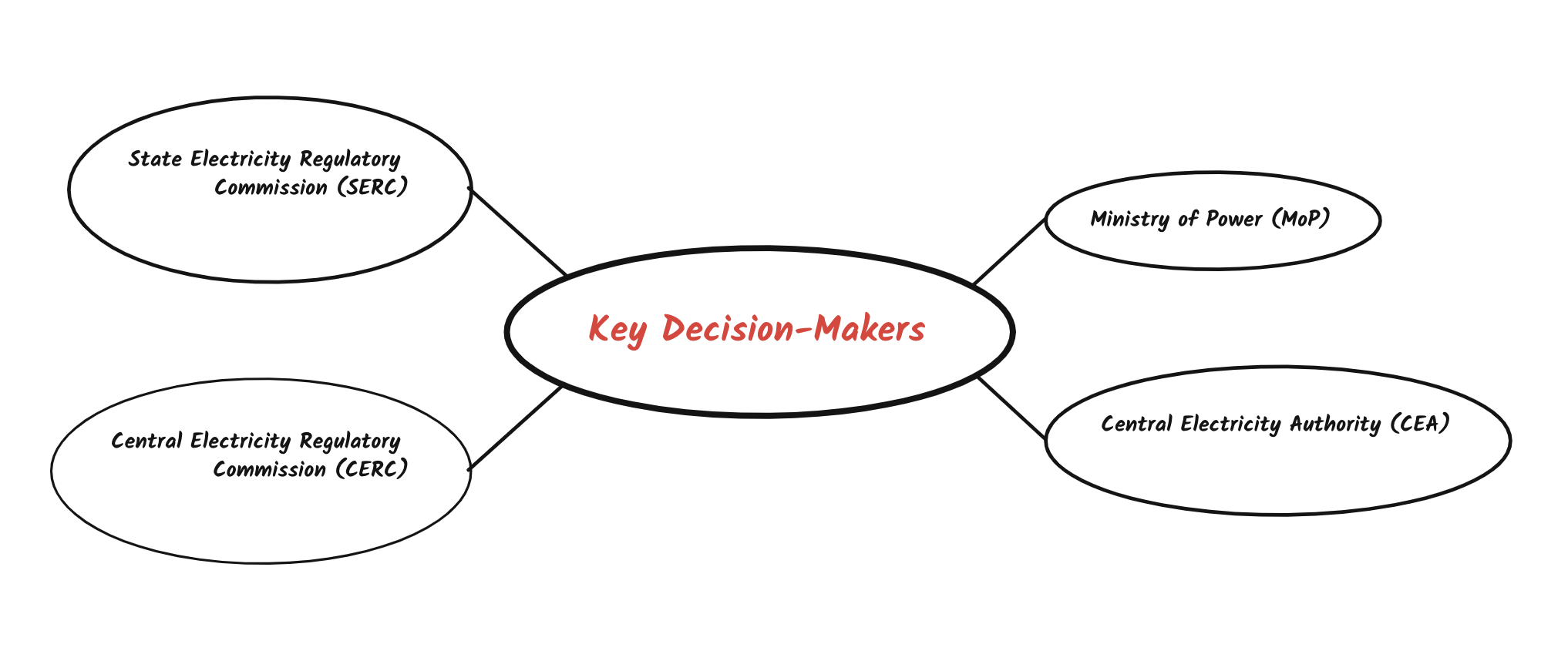
Ministry of Power (MoP) :
It is the nodal agency for Indian Power Sector. It takes the decisions for formulating policies, plans & programs.
Policies – Generation, Transmission, Distribution & for Electricity Consumption.
Plans & Program for the development of power sector.
MoP also regulates the power sector & ensures the availability of reliable and affordable power to all the consumers.
Central Electricity Authority (CEA) :
CEA is a statutory organising body under Ministry of Power. CEA is responsible for advising the government upon Generation, Transmission & Distribution of Electricity.
CEA has different functions :
- Advises the government on matters related to power sector.
- Conducts study & research on power sector.
- Prepare plans & programs for development of india’s electricity sector.
- Monitors the performance of power sector.
- Provides technical assistance to power sector.
Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) :
CERC is an independent regulatory body under Ministry of Power. Responsibilities & Functions of CERC.
It is responsible for setting of tariffs for Electricity Generation, Transmission & Distribution.
It ensures the quality of power supply.
It regulates the terms and conditions of the licences issued to various entities in the power sector.
It promotes the competition in the power sector.
It ensures the quality, continuity, and reliability of power supply.
It protects the interests of consumers.
State Electricity Regulatory Commission (SERC) :
SERC is also an independent regulatory body under Ministry of power. Responsibilities & Functions of SERC.
It determines the methodology for calculating and fixing tariff for Electricity Generation, Transmission & Distribution within their respective states.
It determines the methodology for determining the return on investments(ROI) in generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity.
It regulates the terms and conditions of the licences issued to various entities in the power sector.
It promotes competition in the power sector.
It ensures the quality, continuity, and reliability of power supply.
It protects the interests of consumers.
It resolves disputes between consumers and power companies.
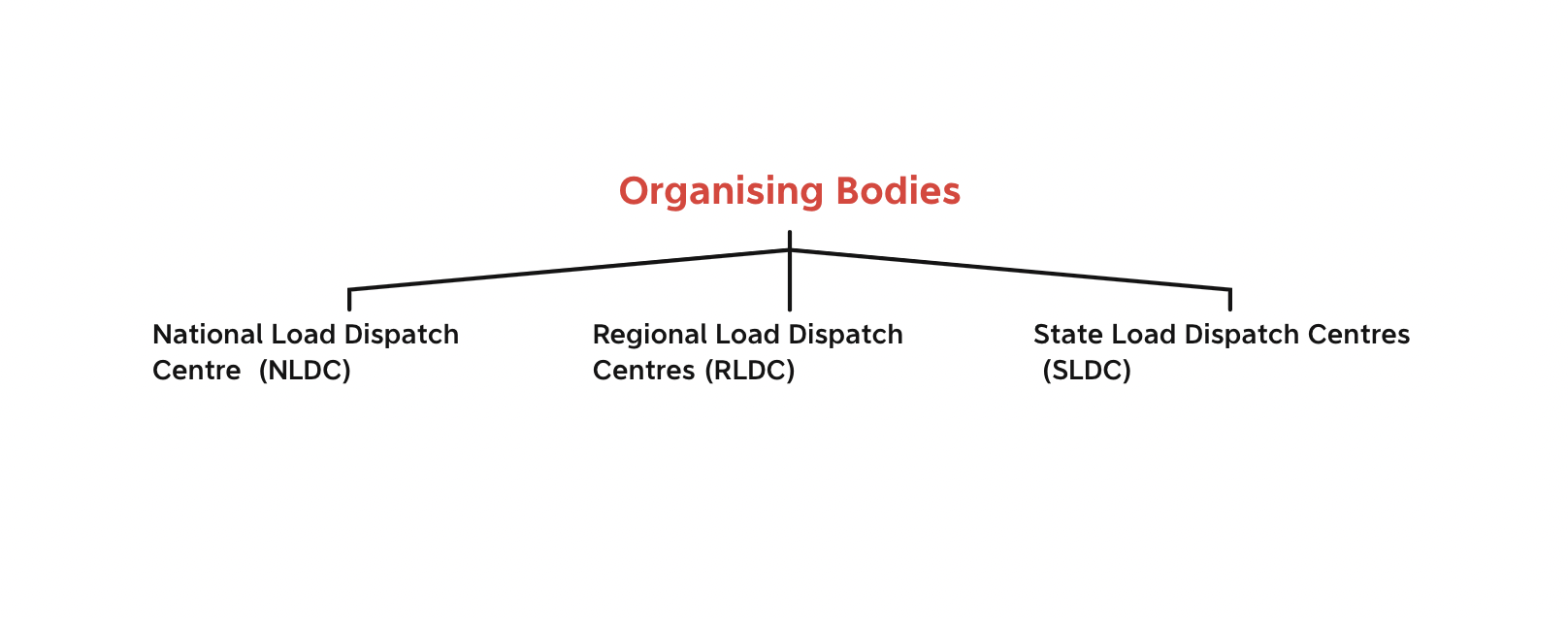
National Load Dispatch Centers (NLDC) :
NLDC is the apex load dispatch center in india. Its is responsible for integrated operations of power system. NLDC is located in New Delhi.
Responsibilities & Functions of NLDC:
It monitors the power system (i.e generation, transmission & distribution of energy) in real time.
It manages the power system to ensure that the demand and supply of electricity are balanced.
It controls the power system to ensure that the demand and supply of electricity are balanced.
Communicates with stakeholders, such as power generation companies, power transmission companies, and power distribution companies.
It schedule and dispatch electricity within the Indian power system.
It provides the operational feedback for national grid planning.
Regional Load Dispatch Centers (RLDC) :
There are 5 RLDCs in india. They looks after their respective regions. RLDCs are located in New Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai & Guwahati.
Responsibilities & Functions of RLDC:
Monitoring the power system within their respective region.
Managing the power system.
Controlling the power system.
Communicating with stakeholders.
Scheduling and dispatching electricity.
Providing operational feedback for regional grid planning.
There are 28 SLDCs in india. They looks after their respective states. SLDCs are located in all the states.
Responsibilities & Functions of SLDC:
Monitoring the power system within their respective state.
Managing the power system.
Controlling the power system.
Communicating with stakeholders.
Scheduling and dispatching electricity.
Providing operational feedback for states grid planning.
List of key organizing bodies for renewable energy in India:
Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE):
The MNRE is the nodal ministry for all matters relating to renewable energy in India.
It is responsible for formulating policies, plans and programs for the development of renewable energy.
The MNRE also provides financial and technical assistance to renewable energy projects.
National Renewable Energy Agency (NREA):
The NREA is an autonomous body under the MNRE.
It is responsible for implementing the renewable energy programs of the MNRE.
The NREIndia also provides information and technical assistance to renewable energy developers.
Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI):
The SECI is a public sector enterprise under the MNRE.
It is responsible for implementing the solar power programs of the MNRE.
The SECI also provides financial assistance to solar power projects.
Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA):
The IREDA is a financial institution under the MNRE.
It provides financial assistance to renewable energy projects.
National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE):
The NISE is an autonomous body under the MNRE.
It is responsible for conducting research and development in solar energy.
The NISE also provides training and capacity building in solar energy.
National Clean Energy Fund (NCEF):
The NCEF is a corpus fund set up by the MNRE to promote renewable energy projects.
The NCEF provides financial assistance to renewable energy projects that are not commercially viable.
National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE):
The NIWE is an autonomous body under the MNRE.
It is responsible for conducting research and development in wind energy.
NIWE also provides training and capacity building in wind energy.
National Biomass Power Agency (NBPA):
The NBPA is an autonomous body under the MNRE.
It is responsible for promoting biomass power projects in India.
The NBPA provides financial assistance and technical support to biomass power developers.
Solar Energy Foundation of India (SEFI):
The SEFI is a non-profit organization that promotes the use of solar energy in India.
The SEFI provides information and technical assistance to solar energy developers.
India Solar Association (ISA):
The ISA is a non-profit organization that represents the solar industry in India.
The ISA works to promote the growth of the solar industry in India.
Conclusion:
The Indian power sector is a complex and dynamic sector. It is responsible for generating, transmitting, and distributing electricity to all consumers in India. The sector is made up of a number of different players, including government agencies, private companies, and non-governmental organizations.
The decision-makers and key players in the Indian power sector play a vital role in ensuring the reliable and affordable supply of electricity to all consumers. They are responsible for formulating policies, setting tariffs, and regulating the sector.
The Indian government has taken a number of steps to promote renewable energy in India. These include setting ambitious targets for renewable energy generation, providing financial and technical assistance to renewable energy projects, and creating a favorable regulatory environment for renewable energy. “power industry report”
The future of the Indian power sector is bright. With the increasing demand for electricity and the government’s focus on renewable energy, the sector is poised for growth.




List of Solar Power Plants in India | Top 10 Largest Solar Power Plants in India - swincorp
[…] Previous Blog : Indian Power Sector Analysis […]
CNG Full Form - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Advantages of Wind Energy - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Is India Ready for Electric Vehicles - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis Disadvantages of Hydropower […]
Best Rooftop Solar Panels for Your Home: A Complete Guide - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
G20 Summit 2023: A Turning Point for the Global Economy - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
JSW Energy Share Price: What to Expect in 2023 - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Disadvantages of Hydropower | Swincorp Energy - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Top 5 Best Solar Lights for Your Home | Swincorp Energy - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
The Rise of Wind Energy in India | Swincorp Energy - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Why Nuclear Energy Is Not as Widely Used as You Think - swincorp
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
India's Largest Hydropower Plant : Koyna Hydroelectric Project - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
How Does Wind Energy Work : Free Complete Guide - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
3KW Solar Power System 2023: Cost, Subsidy. - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Advantages of Geothermal Energy - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Suzlon Share Price - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Solar Cell Types - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Solar Panel Manufacturing : Process, Production Stages - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Solar Panel Efficiency And Performance Metrics - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Solar Trackers : Types, Pros, Cons | Swincorp Energy - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Maruti Brezza CNG: Mileage, Review, Features - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
Tata Punch EV: On Road Price, Range, Review - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]
MG Comet EV - Features, Specs & Everything You Need to Know (2024) - Swincorp Energy
[…] India’s Power Sector Analysis […]