Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy, the heat emanating from the Earth’s core, offers a clean, reliable, and sustainable solution for our energy needs. It’s no passing fad; humans have harnessed this natural power for centuries, from soaking in hot springs to heating homes. But today, geothermal technology is taking center stage, offering a glimpse into a greener and more secure energy future.
What is Geothermal Energy?
Imagine the Earth as a giant pot of simmering lava. The heat from this molten core radiates outwards, warming surrounding rocks and creating vast reservoirs of hot water and steam. Geothermal energy taps into this heat, using it to generate electricity or directly for heating and cooling purposes.
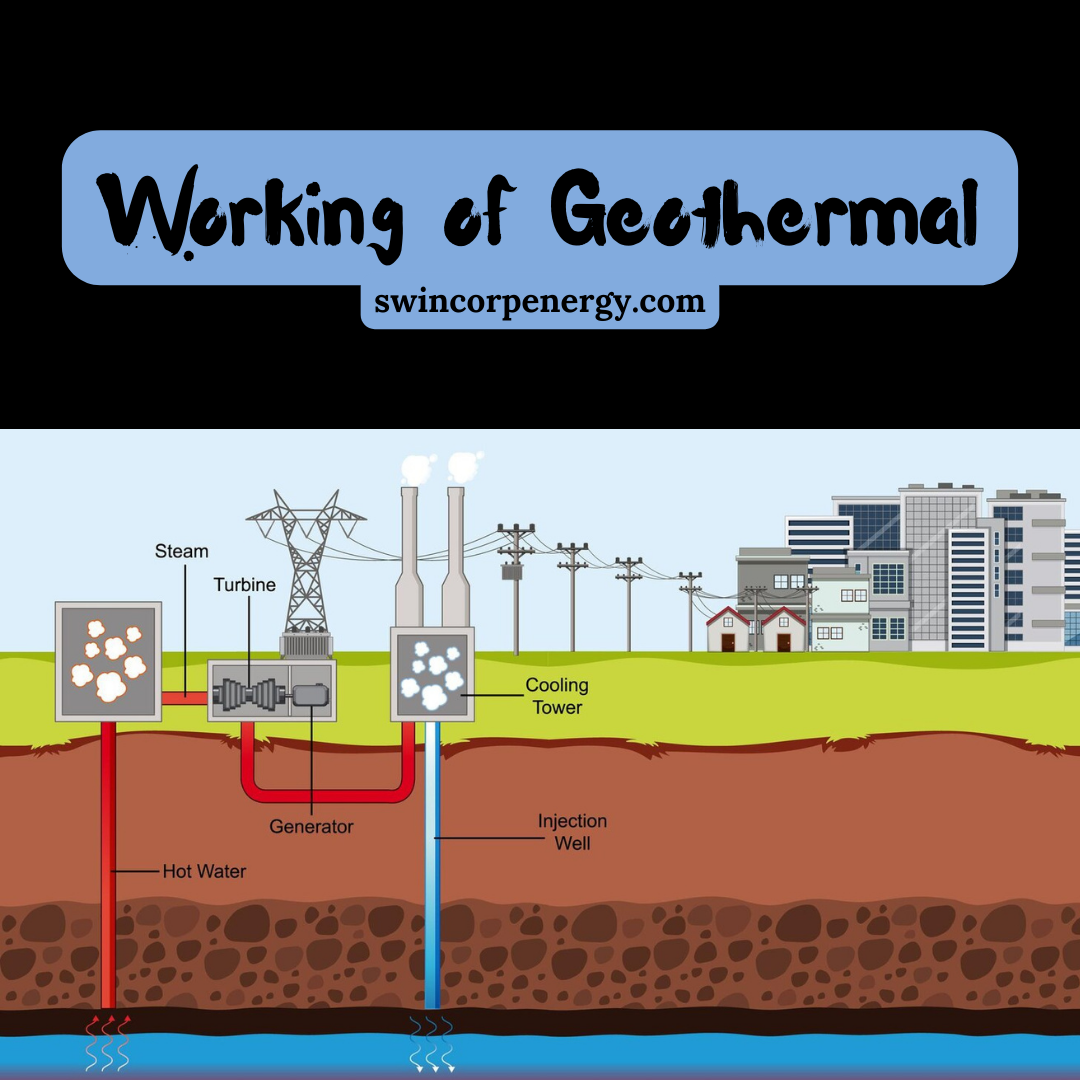
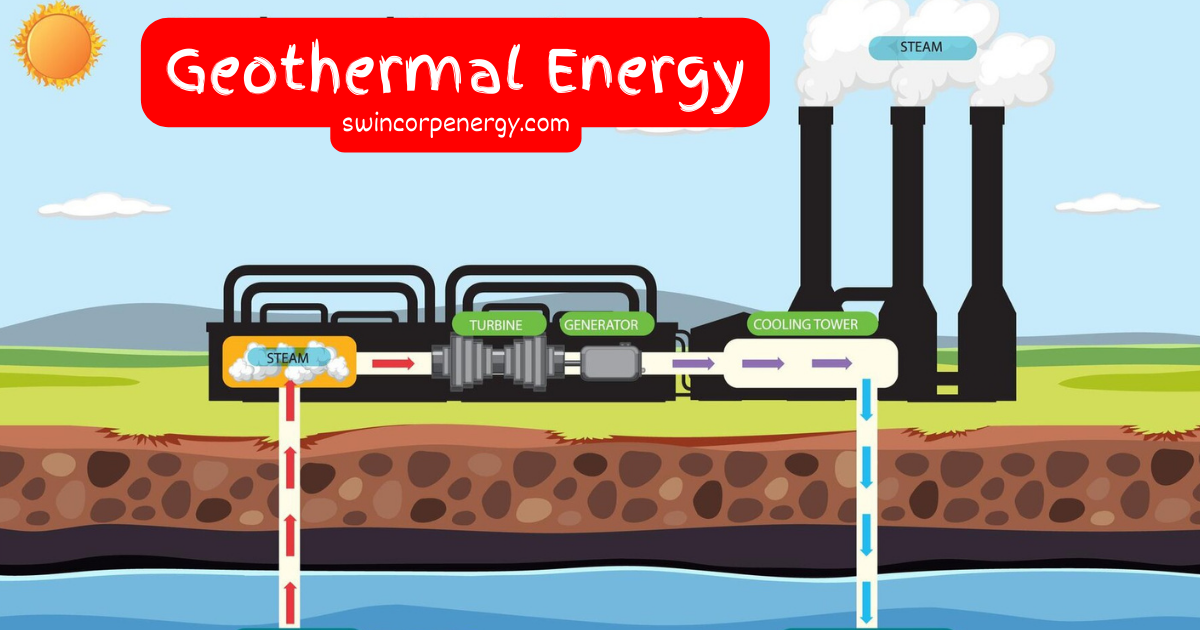
How Does it Work?
There are two main ways to utilize geothermal energy:
Electricity Generation:
- Dry steam: Hot steam from the reservoir is used to directly drive turbines, generating electricity. This is the most mature technology but requires specific geological conditions.
- Flash steam: Hot water from the reservoir is flashed into steam at lower pressure, driving turbines. This is more efficient than dry steam plants but may require additional water injection.
- Binary cycle: In this closed-loop system, a secondary fluid with a lower boiling point is heated by the geothermal fluid. This secondary fluid then boils and drives turbines, generating electricity. This method is more versatile and can utilize lower-temperature resources.
Direct Use:
- Geothermal Heat Pumps: These systems extract heat from shallow ground sources to heat buildings and provide hot water.
- District Heating: Hot water from geothermal sources is piped to heat entire neighbourhoods or communities.
- Industrial Applications: Geothermal energy powers greenhouses, food drying facilities, and other industrial processes.
Geothermal Energy Advantages and Disadvantages
- Renewable: Unlike fossil fuels, geothermal energy is constantly replenished by the Earth’s heat.
- Clean: Geothermal power plants produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Reliable: Geothermal energy is not dependent on weather conditions, providing a stable and predictable source of power.
- Baseload Power: Geothermal plants can operate 24/7, providing crucial baseload power for grids.
- Domestic Resource: Geothermal potential exists in many countries, reducing reliance on imported fuels.
While promising, geothermal energy faces challenges:
- Upfront Investment: Initial drilling and infrastructure costs can be high.
- Geographic Limitations: Suitable geothermal resources are not evenly distributed worldwide.
- Technology Development: Advanced technologies are needed to harness deeper and hotter resources.
Despite these challenges, the future of geothermal energy is bright. Technological advancements, coupled with supportive policies, are driving down costs and expanding accessibility. As the world transitions towards clean energy, geothermal energy is poised to play a vital role in powering a sustainable future.
RELATED POSTS:
- Advantages of Wind Energy
- CNG Full Form
- Suzlon Energy share price
- Top 10 Largest Solar Power Plants in India
- India’s Power Sector Analysis
- 3KW Solar System Cost
- JSW Energy Share Price
- Solar Mounting Structures
- Advantages of Nuclear Energy
- G20 Summit Countries
- Choose the Right Battery Energy Storage
- How Hydropower Plants Work ?
Renewable energy, Clean energy, Baseload power, Direct use, Electricity generation, Geothermal power plant, Flash steam, Binary cycle, Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS), Geothermal reservoir, Hot spring, Geyser, Geothermal heat pump, District heating, Sustainable energy, Carbon-free energy, Geothermal energy policy, Investment in geothermal, Future of geothermal energy, Environmental impact of geothermal energy