India's Largest Hydropower Plant : Koyna Hydroelectric Project

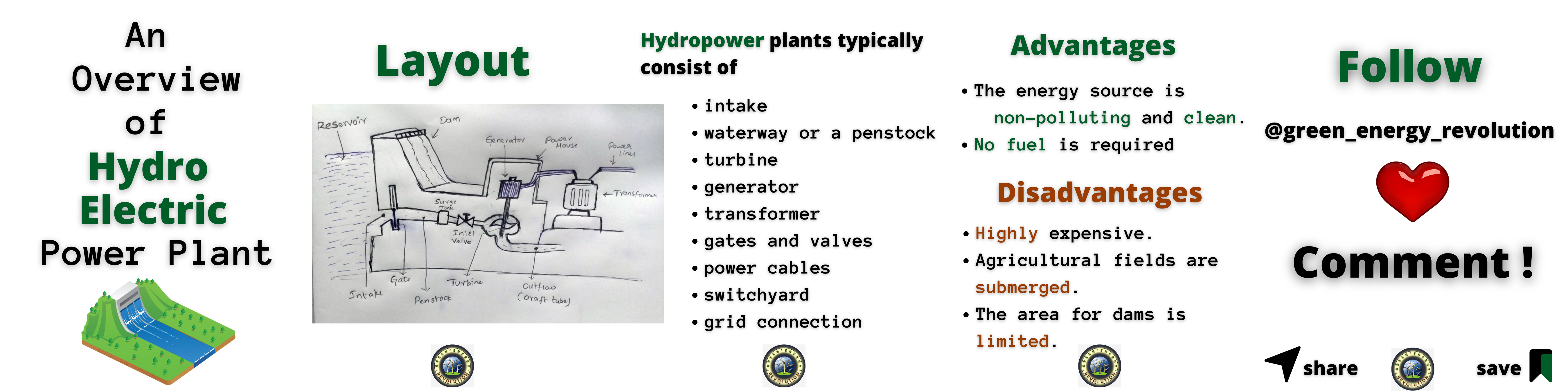
How Hydropower Plants Work ?
Hydropower plants work by converting the kinetic energy of flowing water into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy. This is done using a turbine and a generator.
The turbine is a device that rotates when water flows through it. The blades of the turbine are turned by the force of the water, which causes the turbine to spin. The turbine is connected to a generator, which is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
As the turbine spins, it turns the shaft of the generator. The generator’s shaft is connected to a rotor, which is a spinning magnet. The rotor spins inside a stator, which is a stationary coil of copper wire. As the rotor spins, it creates a magnetic field that changes the flow of electrons in the stator. This flow of electrons is electricity.
India's Largest Hydropower Plant : Koyna Hydroelectric Project
The Koyna Hydroelectric Project is the largest hydroelectric power plant in India, with a total installed capacity of 1960 MW. It is located in the Satara district of Maharashtra, on the Koyna River. The project is a complex one, with four dams and four underground powerhouses. The Koyna Hydroelectric Project plays an important role in meeting India’s growing electricity demand, and it is a vital source of renewable energy for the country.
History of the Koyna Hydroelectric Project
The Koyna Hydroelectric Project was constructed in the 1960s by the Maharashtra State Electricity Board (MSEB). The project was completed in 1964, and it began generating electricity in 1965. The Project was one of the first major hydroelectric power plants to be constructed in India, and it is a landmark project in the country’s history of renewable energy development.

Design and Operation of the Koyna Hydroelectric Project
The Koyna Hydroelectric Project is a complex system that consists of four dams, four powerhouses, and a network of tunnels and canals. The four dams are the Koyna Dam, the Shivaji Sagar Dam, the Warna Dam, and the Kalammawadi Dam. The four powerhouses are the Koyna Powerhouse, the Shivaji Sagar Powerhouse, the Warna Powerhouse, and the Kalammawadi Powerhouse.
The Koyna Hydroelectric Project works by using the kinetic energy of the Koyna River to generate electricity. The water from the Koyna River is stored in the four dams. When the water level in the dams reaches a certain level, the water is released through a network of tunnels and canals to the four powerhouses. The water drives turbines at the powerhouses, which generate electricity. The electricity is then transmitted to the grid and distributed to consumers.
Benefits of the Koyna Hydroelectric Project
The Koyna Hydroelectric Project has a number of benefits, including:
- Renewable energy source: Koyna Project is a renewable energy source, meaning that it can be replenished naturally. Hydropower is a clean and sustainable source of energy, and it does not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants.
- Reliable energy source: The Koyna Project is a reliable energy source, meaning that it can generate electricity consistently, even when the wind is not blowing or the sun is not shining. Hydropower plants can also be used to store energy, which can be helpful for balancing the grid.
- Flood control: This Project also provides flood control benefits. The dams at the project help to regulate the flow of the Koyna River, which reduces the risk of flooding downstream.
- Irrigation: The Koyna Hydroelectric Project also provides irrigation benefits. The water from the dams is used to irrigate crops in the surrounding areas.
Challenges of the Koyna Hydroelectric Project
The Koyna Hydroelectric Project also faces some challenges, including:
Environmental impact: The Koyna Hydroelectric Project has been criticized for its negative impact on the environment. The construction of the dams and the operation of the powerhouses have disrupted fish migration and harmed aquatic ecosystems.
Safety concerns: The Koyna Hydroelectric Project is located in an earthquake-prone area, and it has experienced a number of earthquakes over the years. This has raised concerns about the safety of the project.
Conclusion
- The Koyna Hydroelectric Project is the fourth largest hydroelectric power plant in Asia.
- The project has a total water storage capacity of 277.5 cubic kilometers.
- The project generates an average of 9000 million units of electricity per year.
- The Koyna Hydroelectric Project has been awarded the Indira Gandhi Paryavaran Puraskar, India’s highest environmental award, for its commitment to environmental protection.
The Koyna Hydroelectric Project is a testament to India’s commitment to renewable energy development. It is a vital source of clean and sustainable energy for the country, and it plays an important role in meeting India’s growing electricity demand.
READ OUR PREVIOUS ARTICLES:
List of Solar Power Plants in India | Top 10 Largest Solar Power Plants in India
Disadvantages of Hydropower
Is India Ready for Electric Vehicles ?
Best Rooftop Solar Panels For Home
Best Solar Lights for your Home
Keys: Koyna Hydroelectric Project | India’s Largest Hydropower Plant Koyna Dam | Shivaji Sagar Dam | Warna Dam | Kalammawadi Dam Koyna Powerhouse | Shivaji Sagar Powerhouse | Warna Powerhouse | Kalammawadi Powerhouse Hydropower | Renewable energy | Clean energy | Sustainable energy Electricity generation | Flood control | Irrigation Maharashtra | Satara district | Western Ghats | Earthquake-prone area Environmental impact | Safety concerns | Indira Gandhi Paryavaran Puraskar

3KW Solar Power System 2023: Cost, Subsidy. - Swincorp Energy
[…] How Hydropower Plants Work ? […]
Disadvantages of Hydropower | Swincorp Energy - Swincorp Energy
[…] How Hydropower Plants Work ? […]
Solar Panel Manufacturing: Process, Production Stages - Swincorp Energy
[…] How Hydropower Plants Work ? […]
Solar Panel Efficiency And Performance Metrics - Swincorp Energy
[…] How Hydropower Plants Work ? […]
Maruti Brezza CNG: Mileage, Review, Features - Swincorp Energy
[…] How Hydropower Plants Work ? […]
MG Comet EV - Features, Specs & Everything You Need to Know (2024) - Swincorp Energy
[…] How Hydropower Plants Work ? […]